
Month: March 2018


Structure of molecules
It is freaking amazing that the structure how we look at molecules is also how they are for real as you can see in the next picture.
Explanation of the visualisation technique:
It’s basically a very sensitive needle that is moved over a surface and is repelled by any electron density. The movement of the needle is recorded as a digital signal and thus a graphical representation of electron density can be created.
How does bronchus obstruction lead to hyperinflation?
Bronchusobstruction in Asthma en COPD leads to hyperinflation of the lung. Bronchusobstruction mainly leads to problems in exhaling instead of inhaling. I never understood this.
Because if bronchusobstruction exists, surely inhaling and exhaling must be equally problematic right? I will try to explain in this blogpost why bronchusobstruction mainly results in exhaling-problems.
Analogy:
Normal physiology of breathing:
To ventilate the lungs the lungs must expand (inhalation) en contract (exhalation) in a cyclical manner.
Inhalation: to expand the lungs the diaphragm contracts and pulls the base of the lungs downward. Increasing the volume decreases the pressure. This is according to Boyle’s law: P * V = constant.
During inhalation the pressure in the lungs are decreased because of thorax expansion. By expanding the thorax, you are also expanding the airways inside the thorax. Low pressure inside the thorax prevents the airways from collapsing.
Exhalation: allthough inhalation is an active process, exhalation is a passive process during rest. The lung consists of elastic tissue. Because of elasticity of the lung tissue, the lung constantly wants to contract. The lungs are like an elastic band that are stretched during inhalation and automatically contracts causing exhalation.Thus exhalation causes no physical energy and is considered passive.
If you are inhaling or exhaling, the inward force of elasticity of lung matches the outward force of the thorax. The volume of the lung becomes stable and this is called the Functional Residual Capacity of the lung. This is shown in the next image:
Thus, loss of elasticity of the lungs leads to worse lung contraction and worse exhalation.
During exhalation the pressure in the lungs are increased and the alveoli correctly and the airway pathologically are closed.
Dynamic airway collapse because of high-pressure active exhalation:
Active exhalation is done by using the abdominal muscles to force the diafraghm upwards and internal intercostal muscles. However, this maneuver also reduces the diameter of the bronchi, limiting the rate at which they can exhale.
- Loss of elasticity
- Dynamic airway collapse caused by 1.
- Loss of diaphragm function/curvature because of hyperinflation by 1. and 2.


Extra-thoracic obstruction: (croup, epiglottis, trachea tumor): The trachea tends to collapse during inspiration below the site of obstruction during inspiration because pressures in the extrathoracic trachea fall below atmospheric pressure in the surrounding air.
Intrathoracic obstruction is most severe during expiration and is relieved during inspiration. Extrathoracic obstruction is
Diameter and Poiseulle’s Law
Diameter effect on resistance is quadratic. R=c L/D^4 (Poiseulle’s Law). Thus if you increase the diameter twice in size, the resistance will decrease with


Nice image about derivation

Coincidental

The paradoxical succes of statistical mechanics
So the problem to apply classical mechanics to every particle in a gas is that there is just too many particles and collisions going on. Any degree of uncertainty would immediately exponentionally grow.

{Uncertianity goes exponentially for each application of classical law}
{Uncertainty decreases exponentially for a statistical law}
The accuracy of statistics is, however, rises with increasing numbers. So even though increasing numbers decreases the accuracy of applying mechanics, it increases the statistics. The fact that there are billions and billions collisions and particles going on in a gas is advantegous for applying statistics! This is because it evens out the uncertainty or bias.
You dramatically decrease the precision of classical mechanics, but you dramatically increase the precision of statistical mechanics!

Is the cosmic background just the same as the blue sky?
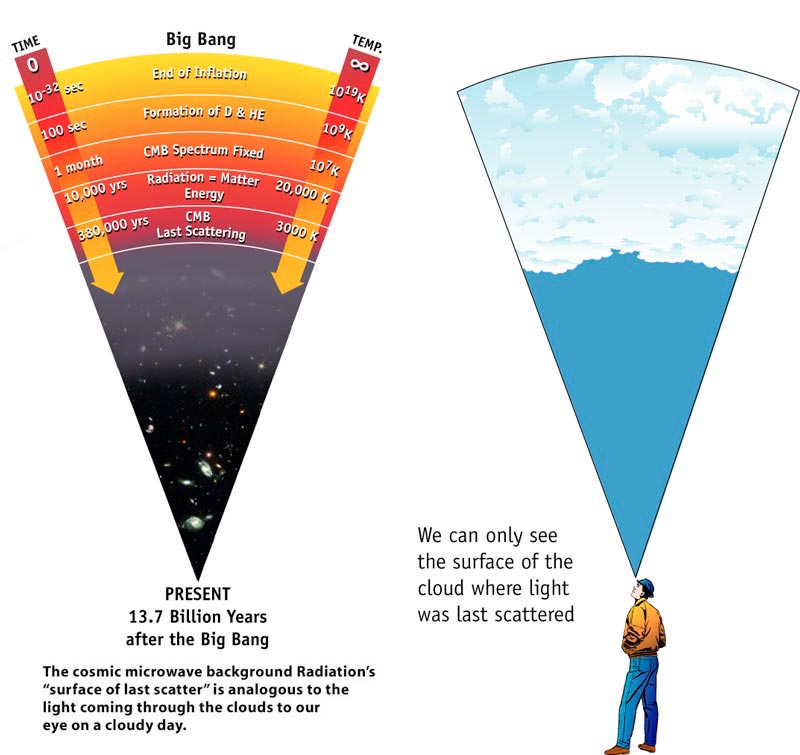
In that sense the blue sky hides what is above, and the cosmic background radiation hides what is in the past.
